Inquiry
Form loading...
- Phone
- E-mail
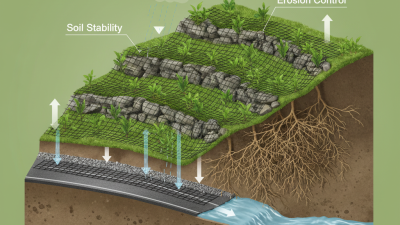
In the realm of civil engineering and construction, the effectiveness of soil support is paramount, particularly in areas prone to erosion and landslides. One innovative solution that has garnered attention is the Geogrid Fabric Retaining Wall. This technology not only addresses the critical need for stable soil structures but also enhances the overall efficiency of retaining wall systems. By employing a unique combination of geogrid materials, these retaining walls provide robust support while optimizing the use of available space, making them a preferred choice for many engineering projects.
The application of Geogrid Fabric Retaining Walls is becoming increasingly popular due to their numerous benefits, ranging from improved soil stability to cost-effectiveness in construction. These structures offer a proactive approach to managing earth pressure and controlling erosion, making them suitable for various landscapes, including highways, railroads, and other infrastructural developments. As we delve deeper into the top advantages of Geogrid Fabric Retaining Walls, it becomes evident that they not only meet functional requirements but also contribute to sustainable building practices in an increasingly environmentally conscious world.

Geogrid fabric retaining walls have emerged as a crucial solution in civil engineering, providing effective soil support while enhancing the stability of structures. These walls utilize geosynthetic materials, known for their tensile strength and ability to reinforce soil, which is particularly critical in areas with challenging soil conditions. Recent industry data indicates that the use of geogrid technology can improve load distribution, ultimately reducing the risk of soil failure by as much as 50% compared to traditional retaining wall systems. This functionality allows for greater flexibility in design and can accommodate varied site requirements.
One of the essential aspects of geogrid fabric retaining walls is their ability to manage lateral earth pressures effectively. By integrating geogrids into soil mass, the walls create a large, stable mass that mitigates the forces acting upon it. A study published in the Geotechnical Engineering journal noted that these systems could sustain higher loads without causing excessive deformation, making them ideal for use in steep applications or where space is limited.
Tips: When designing a retaining wall using geogrid fabric, it’s crucial to conduct a thorough geotechnical investigation. Consider the type of soil and potential groundwater conditions, as this will significantly influence the wall's performance. Additionally, ensuring proper installation of the geogrids can optimize their effectiveness, contributing to long-term soil stability. Regular maintenance checks are also recommended to identify any signs of wear or shifting, which can help prevent costly repairs in the future.
Geogrid fabric has emerged as a transformative solution in soil stabilization projects, offering numerous advantages that enhance structural integrity and durability. One of the key benefits of using geogrid in retaining walls is its ability to provide effective soil support through increased load distribution. The unique properties of geogrid materials allow them to interact with the surrounding soil, creating a reinforced structure that can withstand lateral loads and reduce the risk of failures. This reinforced mechanism not only promotes stability but also minimizes soil erosion, ensuring that the retaining walls perform effectively over time.
Moreover, the use of geogrid fabric in construction projects can lead to significant cost savings. By improving soil strength and reducing the need for extensive excavation or deep foundations, geogrid systems can streamline project timelines while lowering material costs. Additionally, the lightweight nature of geogrid fabric makes it easier to handle and install, further contributing to efficiency on job sites. With lower maintenance requirements and an extended lifespan, geogrid systems represent a sustainable choice for soil stabilization that benefits both the environment and the project budget.
| Benefit | Description | Impact on Soil Stability | Cost Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enhanced Load Distribution | Geogrid fabrics help in evenly distributing loads across the soil, reducing localized stresses. | Increases soil load-bearing capacity. | Reduces the need for extensive excavation work. |
| Reinforced Soil Structure | The fabric stabilizes the soil mass, enhancing overall resistance to deformation. | Prevents soil erosion and displacement. | Minimizes future repair costs. |
| Versatile Application | Can be used in various soil types and conditions for different retaining structures. | Adapts to changing soil conditions effectively. | Saves on material costs by being applicable in many scenarios. |
| Reduced Construction Time | Simplifies installation compared to traditional retaining wall methods. | Quickens project timeline, allowing for faster completion. | Lowers labor costs due to quicker installation. |
| Improved Drainage | Facilitates better drainage through designed openings, reducing water pressure on walls. | Enhances the longevity of the retaining structure. | Decreases maintenance and cleaning costs over time. |
| Environmental Sustainability | Uses less material overall, making it a more eco-friendly option. | Minimizes ecological disruption during installation. | Potential for lower regulatory costs due to environmental compliance. |
| Long-term Performance | Designed for durability, maintaining performance over extended periods. | Ensures continual support without significant degradation. | Reduces the frequency of rebuilds or major repairs. |
Geogrid fabric retaining walls have increasingly gained traction as a cost-effective solution for soil support in various construction projects. According to the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA), geogrid walls can offer significant savings compared to traditional retaining wall systems, such as concrete or masonry. These savings arise not only from lower material costs but also from reduced labor and time associated with installation. A study from the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE) reports that using geogrid technology can reduce construction costs by up to 30% while maintaining structural integrity and performance standards.
Additionally, the longevity and durability of geogrid walls contribute to their overall economic advantage. The lifespan of a geogrid structure can exceed 50 years with minimal maintenance, significantly lowering lifecycle costs. Furthermore, a report from the Geosynthetic Research Institute indicates that geogrid fabric acts to effectively distribute loads and increase soil confinement, leading to increased stability in different environments. This durability and efficiency allow for less frequent replacements, making geogrid retaining walls not only a smart initial investment but also a sustainable long-term solution for earth retention needs.
Geogrid fabric retaining walls play a significant role in enhancing environmental sustainability and erosion control. These innovative structures provide effective soil support while minimizing environmental impact. According to a study published by the American Society of Civil Engineers, geogrid reinforcement can reduce soil erosion by up to 50% when compared to traditional retaining wall methods. This reduction is crucial in maintaining soil quality and preventing sediment loss, which is vital for local ecosystems and agricultural productivity.
One of the key benefits of geogrid walls is their ability to stabilize slopes, which in turn helps to prevent landslides and protect water bodies from sedimentation. Research indicates that well-designed geogrid walls can improve water infiltration and reduce runoff, thus contributing to better water quality in nearby streams and rivers. This aspect of geogrid technology not only supports construction viability but also promotes ecological health.
Tips: When considering the installation of geogrid fabric retaining walls, it's essential to assess the site conditions thoroughly. Proper drainage design is critical to enhance the longevity of the structure and prevent soil erosion effectively. Additionally, utilizing native vegetation on the structure's face can provide added stability and further reduce erosion. Engaging with civil engineering professionals can also help in optimizing design for environmental sustainability.
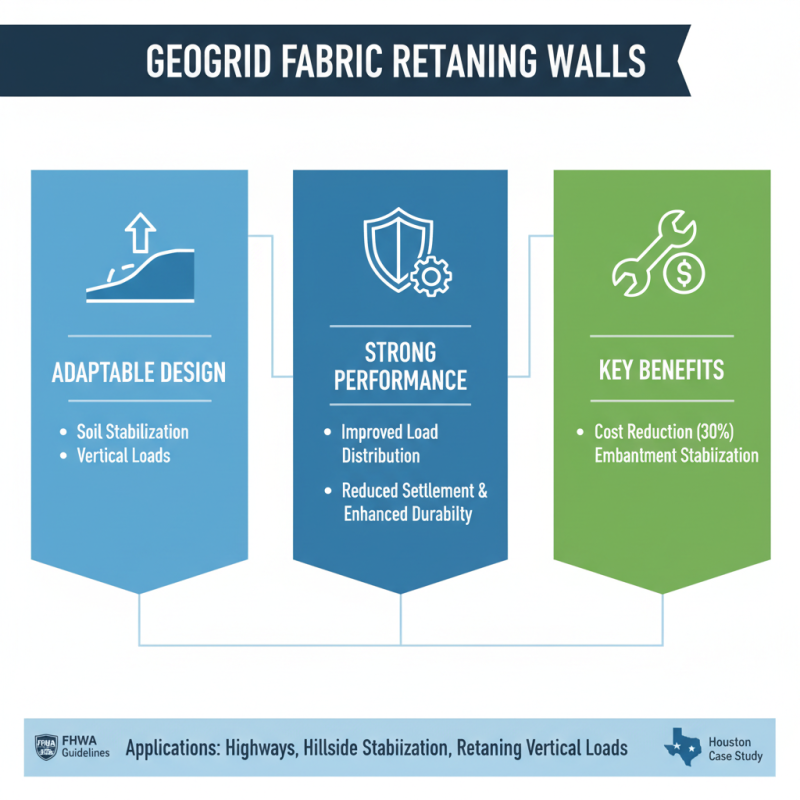
Geogrid fabric retaining walls have gained significant traction in the construction and civil engineering sectors due to their adaptable design and strong performance in soil stabilization. These reinforcing structures are particularly effective in various applications, including highway embankments, hillside stabilization, and retaining vertical loads. According to the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA), the applications of geogrid systems can improve the load distribution across a broad area, leading to reduced settlements and enhanced durability. As engineers increasingly turn to geogrid fabrics, notable case studies underscore their effectiveness. For instance, a project in Houston, Texas, demonstrated a 30% cost reduction and improved soil performance through the implementation of geogrid-reinforced retaining walls in stabilizing a critical embankment.
Another compelling case study highlights the use of geogrid fabric in a major transportation project in California, where it played a pivotal role in preventing soil erosion along the coastal highway. By incorporating geogrids, engineers reported a significant increase in lateral earth pressure resistance, allowing for steeper wall configurations without compromising structural integrity. Data from the Geo-Institute of ASCE indicates that projects employing geogrid technology achieve up to 50% savings in material use when compared to traditional retaining wall systems, further exemplifying the benefits of geogrid fabric in optimizing resource efficiency while ensuring effective soil support. Such evidence not only showcases the capabilities of geogrid technology but also encourages its adoption across diverse engineering applications.