Inquiry
Form loading...
- Phone
- E-mail
Geogrid Ground Grid has transformed the construction industry significantly. As John Smith, a leading expert in geosynthetics, stated, "Geogrid technology enhances stability and reduces costs in construction." This innovation offers numerous benefits that address common challenges in building projects, such as soil instability and resource management.
The inclusion of Geogrid Ground Grid in construction can lead to improved load distribution and soil reinforcement. These advantages result in safer structures and prolonged lifespan. However, one must acknowledge that not all projects may benefit equally. Factors like soil type and project scale can influence effectiveness. Misapplication can lead to setbacks.
Furthermore, understanding the intricacies of Geogrid Ground Grid is essential for successful implementation. Some construction teams may struggle with integration, which can lead to unexpected complications. Recognizing these potential pitfalls can enhance the use of this technology and promote wiser decision-making. Embracing Geogrid Ground Grid offers promise, but awareness of its limitations is equally vital.
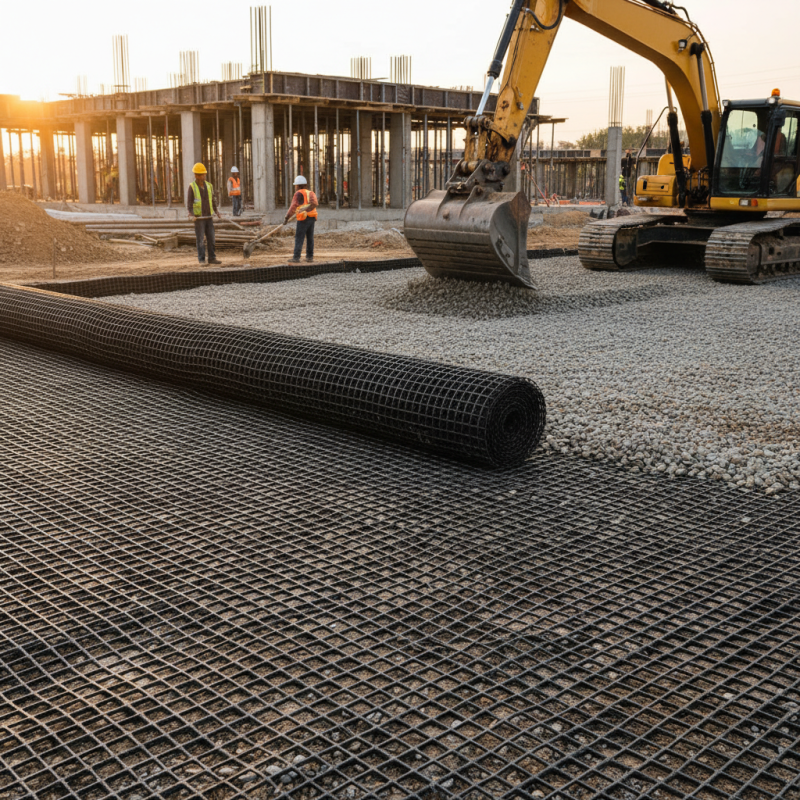

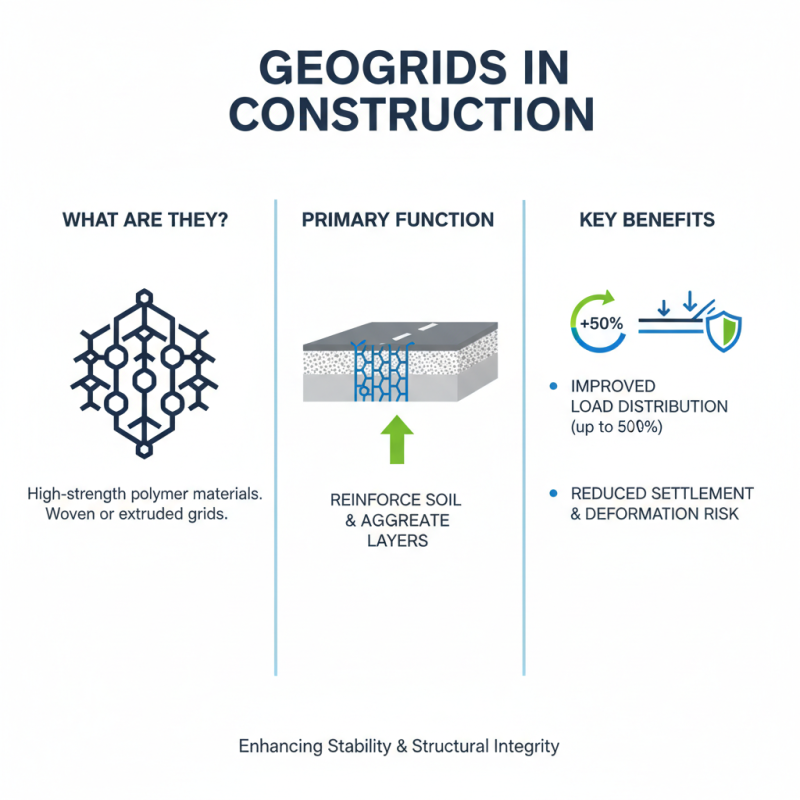
Geogrid ground grids play a pivotal role in construction, enhancing stability and structural integrity. These grids are made from high-strength polymer materials designed to reinforce soil and aggregate layers. Research shows that using geogrids can improve load distribution by up to 50%. This improvement can significantly reduce the risk of settlement and deformation.
The functionality of geogrids is evident in various applications, including roads, retaining walls, and embankments. They provide a reliable method for controlling soil movement. With proper installation, geogrids can increase the lifespan of structures. However, improper use or soil preparation can negate these benefits. It's essential to conduct thorough soil analysis before deployment.
Data from industry reports indicate that projects utilizing geogrids have shown reduced overall construction costs by approximately 20%. This advantage stems from lesser material needs and shorter construction timelines. Yet, some engineers remain skeptical about their long-term effectiveness. Addressing these concerns requires ongoing research and field studies to validate geogrids' performance over time.
Geogrids are increasingly recognized for their ability to enhance soil stability in construction projects. They provide structural reinforcement that helps to distribute loads over a larger area, reducing soil deformation. A recent industry report indicates that projects using geogrids can experience up to 50% less settlement compared to traditional methods. This statistic is significant for construction projects requiring stable foundations.
In addition, the use of geogrids can improve the drainage of water. Well-drained soil reduces the risk of erosion and other related issues. According to a study conducted by the International Geosynthetics Society, geogrids can increase the permeability of soil by 30%. This shows that incorporating geogrids not only stabilizes soil but also enhances its durability, providing long-term benefits.
However, not every project can effectively utilize geogrids. The soil type, project budget, and construction timeline can impact their effectiveness. Some professionals still debate whether the initial investment in geogrids is justified for smaller projects. Thus, thorough analysis and planning are crucial. The benefits are clear, but careful consideration is necessary to ensure optimal performance.
Geogrids are increasingly popular in construction due to cost-effectiveness. They improve soil stability while reducing material use. This leads to lower project costs. By enhancing load distribution, geogrids minimize the demand for additional materials, which is a significant expense saver.
Using geogrid ground grids can help prevent issues like soil erosion and settlement. This means fewer maintenance costs in the long run. However, some projects may experience challenges in selecting the appropriate geogrid type. Poor choice can lead to failures. It is essential to understand the specific needs of each site. Proper evaluation of soil conditions is vital to recognize potential problems.
Contractors may find that training staff on geogrid installation is necessary. Without proper knowledge, installation can be flawed. This may increase costs rather than reduce them. It's crucial to weigh both short-term savings and long-term durability when opting for geogrids. Attention to detail can greatly influence overall project success.
Geogrids are becoming a popular solution in construction for their environmental benefits. They improve ground stabilization and reduce soil erosion. According to the American Society of Civil Engineers, using geogrids can lead to a 30% decrease in material usage. This reduction directly translates to lower emissions and energy consumption.
Using geogrids helps in managing stormwater effectively. Their design allows for better drainage, reducing runoff. Less runoff means fewer pollutants entering our waterways. A study showed that geogrid systems can enhance water absorption by up to 20%. This innovation promotes sustainable construction practices.
Tip: Incorporating geogrids not only supports eco-friendly construction but also reduces long-term maintenance costs. Consider the lifecycle impacts before choosing traditional materials. A thoughtful approach to ground reinforcement can lead to significant environmental gains. Reflecting on the choices made today shapes a greener tomorrow.
Geogrids play a crucial role in improving load distribution for various construction projects. When installed correctly, these grids enhance the stability of base layers. They minimize sediment movement and retain soil materials. This leads to better performance under heavy traffic loads. Roads, parking lots, and other surfaces benefit significantly from geogrid usage. Engineers often notice reduced surface deformation over time.
The enhanced traffic performance with geogrids is remarkable. They help in spreading the weight of vehicles more evenly. This prevents localized failure and increases durability. However, geogrids must be selected based on specific site conditions. Not all geogrids are suitable for every application. Sometimes, improper installation can lead to issues. There may also be challenges in maintenance afterward. Observing these details makes a substantial difference in the project’s success.
Incorporating geogrids into design plans is practical. The grids offer long-term solutions to common construction challenges. Yet, professionals should continuously evaluate their effectiveness on site. Regular assessments ensure they perform as intended. Adaptation to changing conditions is necessary.






