Inquiry
Form loading...
- Phone
- E-mail
Soil instability and erosion are critical challenges faced in various construction and landscaping projects. To mitigate these issues effectively, innovative solutions are crucial. One such solution is the utilization of Geo Grid Mesh, a groundbreaking technology designed to enhance soil stabilization and control erosion. This introduction explores the fundamental principles and applications of Geo Grid Mesh, shedding light on its importance in contemporary civil engineering and environmental management.
Geo Grid Mesh functions by reinforcing the soil structure, providing essential support to maintain its integrity under stress. By distributing loads evenly, it helps prevent soil displacement and degradation, making it an ideal choice for landscapes prone to erosion. The strategic implementation of Geo Grid Mesh in construction sites, roadways, and embankments not only improves the longevity of these structures but also contributes to ecological preservation by minimizing environmental disturbance.
In conclusion, the effective use of Geo Grid Mesh represents a proactive approach to tackling soil erosion and stabilization problems. As we delve deeper into the various applications and benefits of this innovative technology, the potential for improving soil conditions and enhancing landscape stability becomes increasingly evident. Understanding how to implement Geo Grid Mesh effectively is essential for engineers, landscape architects, and environmentalists alike, paving the way for more resilient infrastructure and sustainable land management practices.

Geo grid mesh is an innovative solution that plays a critical role in soil stabilization and erosion control. At its core, geo grid mesh refers to a synthetic material engineered through a network of interconnected polymer elements. This grid system creates a three-dimensional structure that enhances load distribution, allowing it to effectively reinforce the soil beneath, thus preventing deformation and erosion. According to a report from the Geosynthetics Institute, the use of geo grid mesh can reduce soil movement by up to 50%, making it a preferred option for various civil engineering projects.
There are several types of geo grid mesh, each designed for specific applications. For instance, uniaxial geo grids are commonly utilized in applications requiring high tensile strength and load-bearing capacity, such as reinforcing pavements and retaining walls. On the other hand, biaxial geo grids provide multidirectional strength, making them suitable for subgrade stabilization in road construction. A study published in the Journal of Geotechnical Engineering highlights that using geo grid mesh in layered soil systems can improve the bearing capacity by up to 30%, reflecting its effectiveness in soil stabilization efforts. Understanding these types is essential for engineers and land developers aiming to address soil-related challenges efficiently.
| Type of Geo Grid Mesh | Material | Application | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Uniaxial Geo Grid | Polypropylene | Road and pavement construction | Enhances load distribution, prevents rutting |
| Biaxial Geo Grid | High-density polyethylene (HDPE) | Slope stabilization | Improves soil strength, controls erosion |
| Fiberglass Geo Grid | Fiberglass | Reinforcement in weak soils | High tensile strength, resistant to chemical attack |
| Geocell | Polyethylene | Load support for unpaved roads | Reduces material use, stabilizes surfaces |
| Composite Geo Grid | Combination of materials | High performance applications | Enhanced durability and load-bearing capacity |
Soil stabilization is a critical process in both construction and agricultural applications, ensuring that the ground can support structures and crops effectively. According to the International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology, unstable soil can lead to structural failures, causing over 1 billion dollars in damages annually in the United States alone. By employing geo grid mesh techniques, construction projects can enhance the bearing capacity of soils, minimize settling, and prevent erosion, ultimately leading to safer and more resilient infrastructures.
In agriculture, soil stabilization contributes significantly to the improvement of arable land. The World Bank reports that soil degradation affects around 1.5 billion hectares of farmland worldwide, reducing productivity and threatening food security. Utilizing geo grid mesh for soil stabilization can help retain moisture, increase nutrient retention, and improve root penetration, thereby enhancing crop yield. Studies indicate that the implementation of geosynthetics can result in an increase in agricultural production by up to 30%, demonstrating the vital role that soil stabilization plays in both economic growth and environmental sustainability.

Geo grid mesh has emerged as a crucial solution for erosion control, particularly in areas prone to soil movement and degradation. According to the U.S. Geological Survey, approximately 20 billion tons of topsoil are eroded from U.S. farmland each year, significantly impacting agricultural productivity and water quality. The application of geo grid mesh can drastically reduce these figures by providing a structural reinforcement for soil layers, thereby decreasing the potential for soil loss during heavy rainfall or adverse weather conditions.
Studies have shown that geo grid mesh can reduce soil erosion rates by up to 50% when properly installed. The mesh works by creating a stabilizing effect, interlocking with the soil and forming a robust surface that can withstand erosive forces. In addition, data from environmental research indicates that implementing geo grid mesh in slope reinforcement projects can enhance vegetation growth by offering a protective layer for seeds and roots, thus promoting soil health and reducing erosion in the long term. The effective use of geo grid technology not only helps sustain the soil but also supports ecological balance in affected regions.
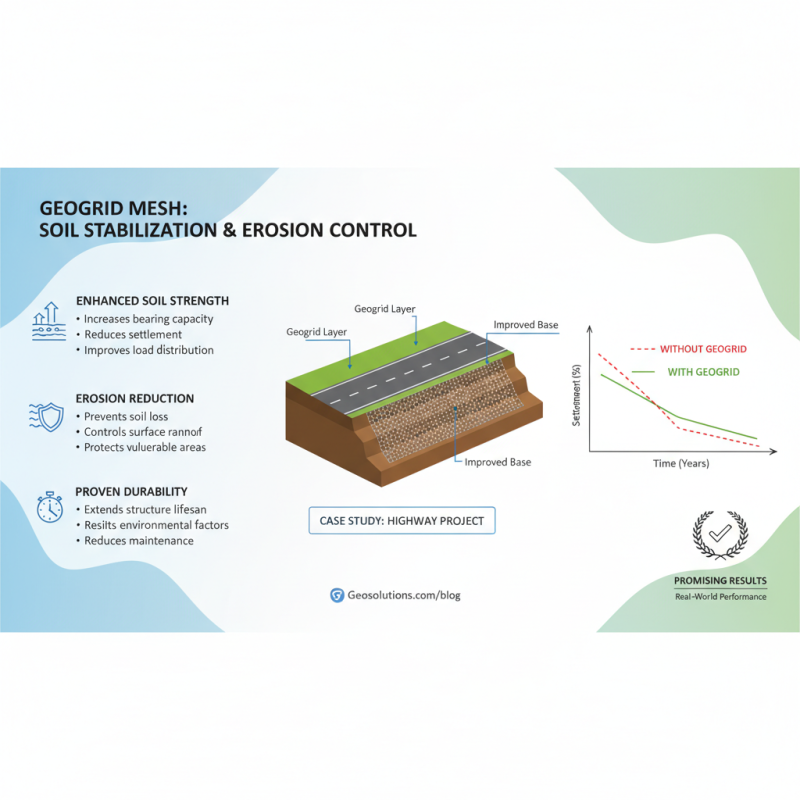
In various real-world projects, the performance metrics of geo grid mesh for soil stabilization and erosion control have demonstrated promising results. Case studies showcase its effectiveness in enhancing soil strength and reducing erosion, particularly in areas prone to environmental degradation. One notable example involved a highway project where the implementation of geo grid mesh significantly decreased the settlement and improved the load distribution, ultimately enhancing the lifespan of the road structure.
Tip: When implementing geo grid mesh, ensure that you assess the site conditions thoroughly. Understanding soil composition and moisture levels can greatly influence the success of soil stabilization efforts.
Another case study illustrated the successful use of geo grid mesh in steep slope stabilization. The project involved retrofitting an existing slope that was experiencing recurrent landslides. By incorporating geo grid mesh, engineers were able to stabilize the slope, thereby preventing further erosion and ensuring safety for nearby infrastructures. Performance metrics from this project highlighted the durability of the geo grid system in increasing the overall stability of slopes in challenging environments.
Tip: Collaborate closely with engineers and geotechnical experts during the planning phase to tailor the geo grid mesh application to the specific environmental conditions of your project.
When it comes to the effective installation of geo grid mesh for soil stabilization and erosion control, understanding various soil conditions is crucial. Soil types can dramatically influence the success of geo grid applications. For instance, sandy soils, which typically have larger particle sizes and lower cohesion, often require deeper anchorage to secure the grid. A study by the Federal Highway Administration indicates that geo grid mesh can improve the bearing capacity of sandy substrates by up to 60% when properly installed. Conversely, clay soils, which can swell or shrink, necessitate careful consideration of moisture levels and grid placement depth, as improper installation can lead to grid deformation or failure.
Best practices also emphasize the importance of site preparation prior to installation. This includes removing organic materials and ensuring a level base, which is vital for achieving optimal stress distribution across the geo grid. The American Society of Civil Engineers recommends compacting the underlying soil to at least 95% of the Proctor density before installing the grid to enhance its performance. Additionally, conducting a soil analysis can provide insights into the soil's shear strength, which is essential for determining the type and configuration of the geo grid mesh needed for a specific project. Following these practices can significantly increase the lifespan and effectiveness of the erosion control measures implemented.






