Inquiry
Form loading...
- Phone
- E-mail
Soil Reinforcement Geogrid is a crucial technology in civil engineering and construction. These geogrids enhance soil stability and strength, making them essential for various applications. According to a 2021 market research report, the global geogrid market is projected to reach $2.5 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 8.5%. This growth reflects the increasing need for infrastructure development and the benefits of geogrid use.
Soil Reinforcement Geogrid works by distributing loads over a larger area, reducing soil deformation. It comprises interconnected polymer or fiberglass materials. An independent study suggests that using geogrids can improve the load-bearing capacity of soil by up to 70%. However, challenges remain. The effectiveness of geogrids may vary depending on soil type and environmental conditions, highlighting the need for careful site assessments.
In practice, while Soil Reinforcement Geogrid offers significant advantages, not all projects have seen success. Some implementations require precise installation techniques. Misalignment can lead to suboptimal outcomes. This calls for engineers to rethink their strategies, ensuring thorough training and preparation.


Soil reinforcement geogrids are vital in construction and civil engineering. They are polyester or polypropylene grids. This structure helps distribute loads. By reducing soil deformation, they enhance stability. These grids are crucial for foundations, slopes, and roadways.
Tips: Ensure proper installation for best results. Misalignment can lead to failures. Always conduct soil assessments beforehand. This helps in choosing the right type of geogrid.
Geogrids improve bearing capacity, but their installation is sensitive. The ground conditions greatly affect performance. A small mistake in laying geogrids can cause serious issues. They require careful handling and an understanding of soil mechanics. When used correctly, they significantly enhance soil strength.
The development of geogrids in soil engineering has transformed how we approach ground stabilization. Initially, engineers relied on traditional methods like soil compaction. However, these methods often failed under extreme conditions. Geogrids emerged in the late 20th century as a more effective solution. They are manufactured from polymers, which provide high tensile strength and flexibility. This innovation opened new avenues for construction, especially in challenging terrains.
When using geogrids, it’s essential to consider the specific requirements of your project. Not all geogrids are created equal. Different types offer varying levels of strength, stiffness, and interface friction. It’s crucial to select the right type based on soil conditions. This choice impacts the overall performance of the soil reinforcement.
Tips: Always conduct a site assessment before implementation. Understanding the soil type is vital. Geogrids can perform poorly if not matched correctly with the soil conditions. Monitor their installation closely to ensure effectiveness. Regular maintenance checks can prevent future complications and enhance stability.
This chart illustrates the increasing usage of soil reinforcement geogrids in soil engineering over the years, highlighting the growing adoption of this technology for enhancing soil stability and performance.
Soil reinforcement geogrid is a crucial tool in soil stabilization. It enhances the load-bearing capacity of soil. Made from durable materials, it provides structural support. When layered within soil, it distributes weight evenly. This reduces the risk of soil erosion and cracking.
The geogrid's grid-like structure allows it to interlock with soil. This interaction enhances soil strength. In practical applications, such as road construction, the benefits are clear. However, the effectiveness can vary depending on soil type. Not all soils react the same way to reinforcement. This variability requires careful planning and testing.
In areas with poor drainage, the geogrid may be less effective. Moist conditions can weaken soil. Users need to consider environmental factors. Mistakes can lead to insufficient stabilization. It is vital to assess conditions before application and adapt methods accordingly. Soil reinforcement geogrid can offer solutions, but precision and attention to detail are essential.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Material Type | Polymer, fiberglass, or geotextile |
| Usage | Used in road construction, embankments, and retaining walls |
| Function | Enhances load distribution and stabilizes soil |
| Benefits | Increases bearing capacity, reduces settlement, and improves durability |
| Installation Method | Typically laid on compacted subgrade and covered with soil |
Soil reinforcement geogrids play a crucial role in construction projects. These materials improve the load-bearing capacity of soil, making them ideal for foundations, roadways, and retaining walls. According to a 2022 industry report, projects that incorporate geogrids can reduce material costs by up to 30%. Engineers appreciate how these grids enhance stability and prevent soil erosion.
Applications of soil reinforcement geogrids include road construction, where they help support heavy traffic loads. A study found that using geogrids can increase pavement life by 50%. In urban developments, geogrids assist in creating tiered landscapes, effectively managing drainage and soil retention. However, while these materials are effective, they can be expensive if not properly integrated.
Geogrids are also used in bridge construction, providing a stronger base. However, the performance of geogrids can depend on soil type and conditions. Insufficient analysis before application may lead to underperforming structures. Construction teams must assess local soil properties to maximize the benefits of geogrids. Awareness of these factors is essential to avoid costly mistakes in project execution.
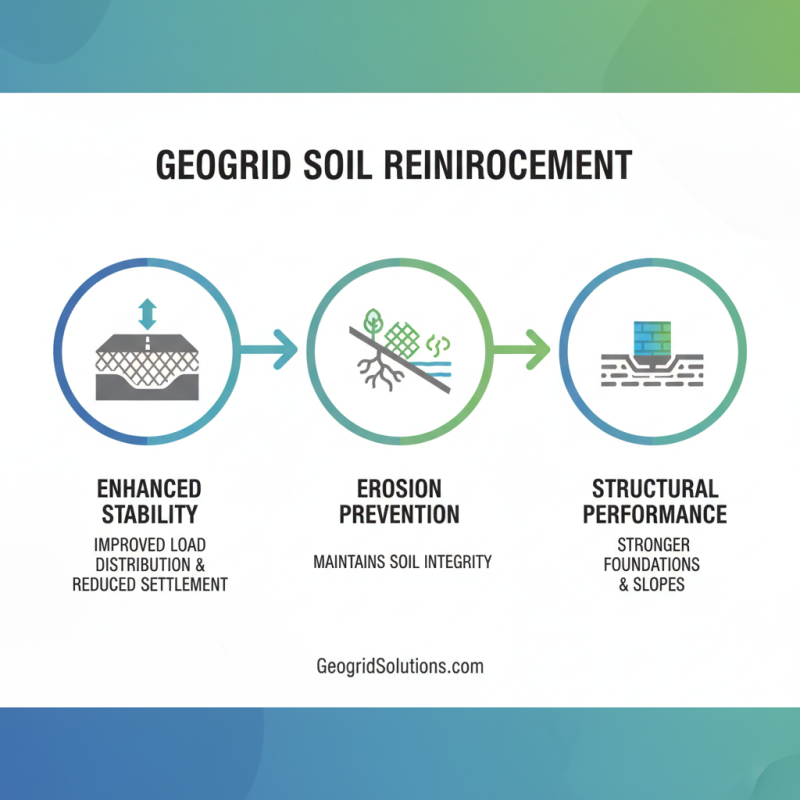
Geogrids are commonly used for soil reinforcement. They provide several benefits in construction and landscaping. One major advantage is stability. Geogrids enhance load distribution in the soil. This leads to reduced settlement and improved performance of structures. They also help prevent erosion by maintaining soil integrity.
However, there are limitations to consider. Geogrid installation can be complex. Proper alignment and tension are crucial. If not installed correctly, the benefits may not be realized. Cost is another factor. While geogrids can save money in the long run, initial expenses can be high. Not every project may justify this investment.
Environmental conditions can also impact their effectiveness. In wet conditions, soil may behave unpredictably. This can lead to failure in reinforcement. It's essential to assess the specific site conditions before deciding on geogrid usage. Awareness of these factors can lead to better outcomes in soil reinforcement projects.






